Subjects, Roles and Permissions
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
The Witboost product implements the role-based access control model as its authorization model.
With role-based access control, users are assigned to roles and permissions are assigned to roles, creating a decoupling between individuals and their permissions. Some strengths of this approach are:
- Flexibility: RBAC allows for a high degree of flexibility in defining roles and permissions. It is easy to add or remove users from roles, or to modify the permissions associated with a role.
- Efficient resource management: RBAC can help organizations manage their resources more effectively by allowing them to define access controls based on the roles of users, rather than on individual users themselves.
- Improved security: By defining access controls based on roles, organizations can ensure that users only have access to the resources they need to do their jobs, which can help to reduce the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information.
To improve performance, we use caching mechanisms for user permissions and scope transformations. These caches help reduce latency and improve the responsiveness of the RBAC system, especially in environments with a large number of users and complex permission structures.
Max cache sizes can be configured in the permission section of the app-config.yaml file. For more details, see the Configuration documentation
RBAC Model
The Role-Based access control implementation in Witboost is composed of the following entities:
- Subjects: that can be a user or a group of users
- Roles: that is a set of permissions with a logical name (e.g.
Data Product Ownerrole) - Permissions: the set of grantable actions available in Witboost
The diagram below summarizes the relationships between these entities:
Configuring RBAC
Roles and permissions must be configured by accessing Administration → Roles & Permissions. To enable this section, a user must have at least one of the following permissions: rbac.role.edit, rbac.role.create or rbac.role.delete. See Rbac permissions
Permissions
In the context of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), a permission is a specific action or set of actions that a user or group (via a role) is authorized to perform.
On Permissions tab a readonly list of all existing permission is provided, with ID, name, and description.
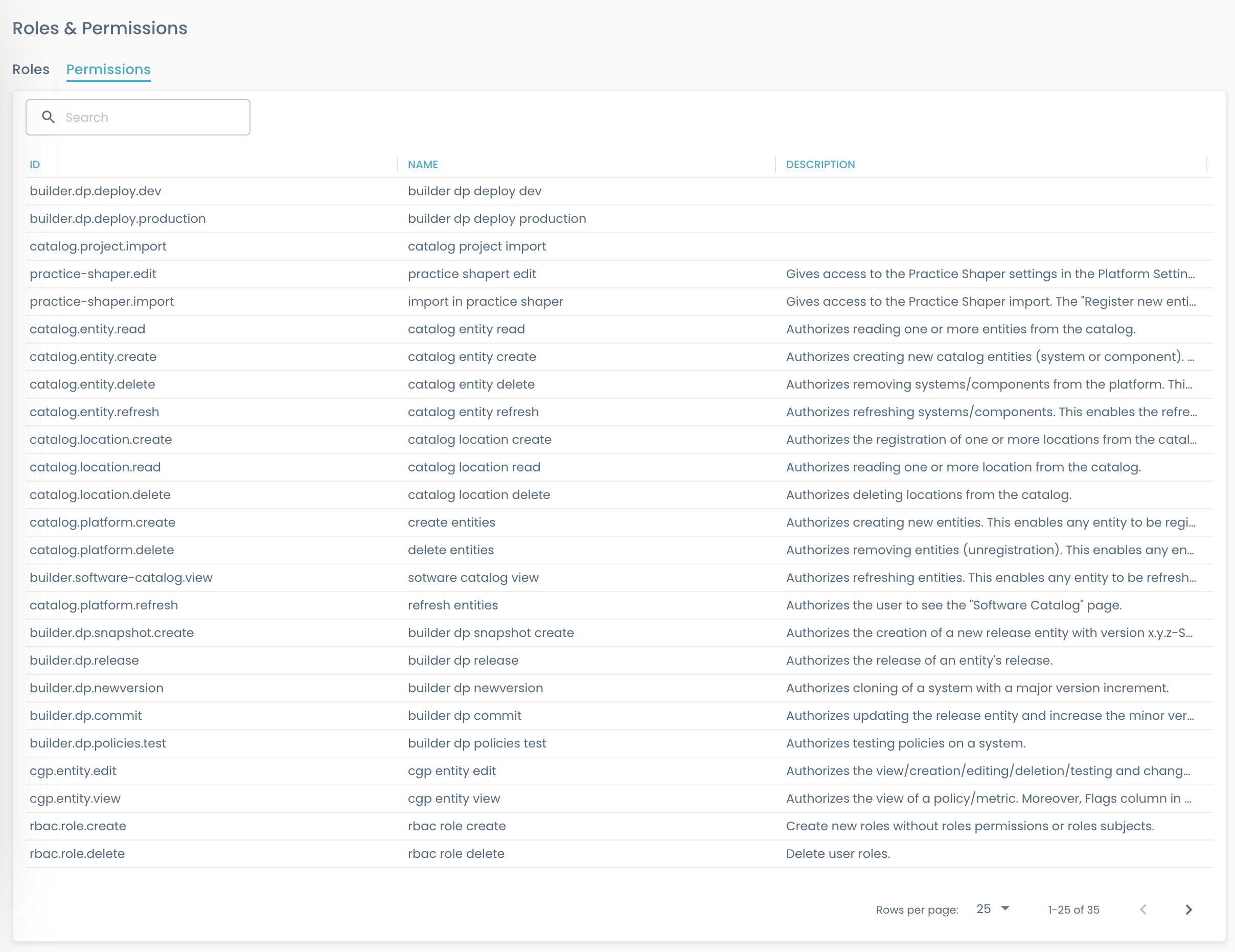
A permission, for example, might allow a user to read a list of systems, execute certain commands on them, or access certain resources in Witboost.
Permissions are typically granted to users or groups through the assignment of roles, which are defined collections of permissions that are then assigned to users or groups to control their access to system resources and functions.
Below we dive into each Witboost module and understand which are all the available permissions. You will also find some cookbooks that facilitate the definition of permissions based on use cases. See the Witboost Permissions list section for a detailed overview all available permissions
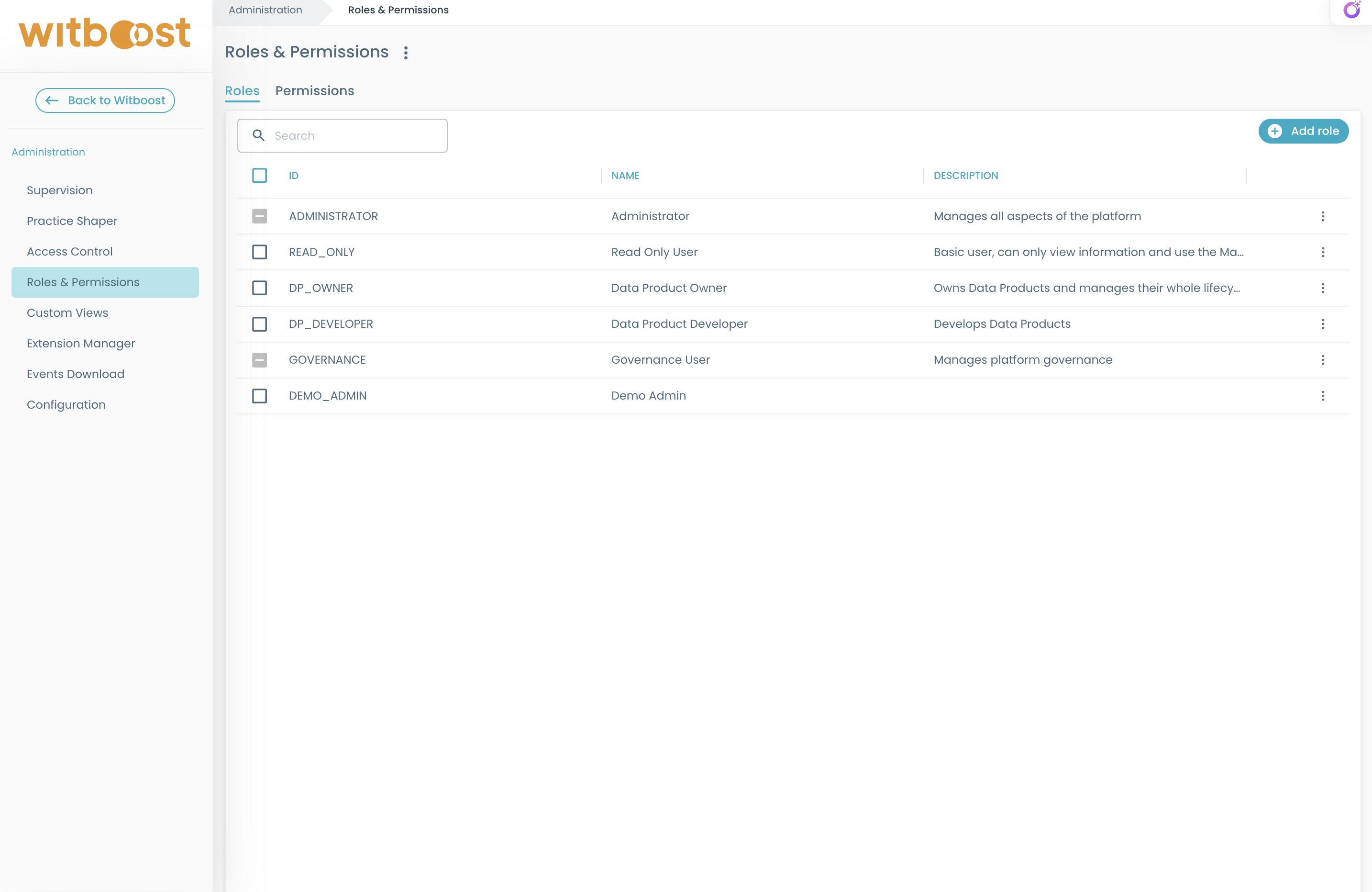
Roles
Roles table displays a list of all roles (both platform and custom) with their ID, name, and description.
id: A unique string identifier of the role, e.g.DP_OWNER. This is auto-generated based on namename: A prettier role identifier or human-readable name for display purposesdescription(optional): A description of the role, for display purposes
Platform roles: are pre-existing roles. Name and description aren't editable and these roles aren't deletable. it's possible to manage assignments and permissions
Custom roles: are created by a user with the rbac.role.create permission. It's possible to edit information, delete the role, and manage assignments. Custom roles are created through a drawer opened by clicking the "Add Role" button in the table header.
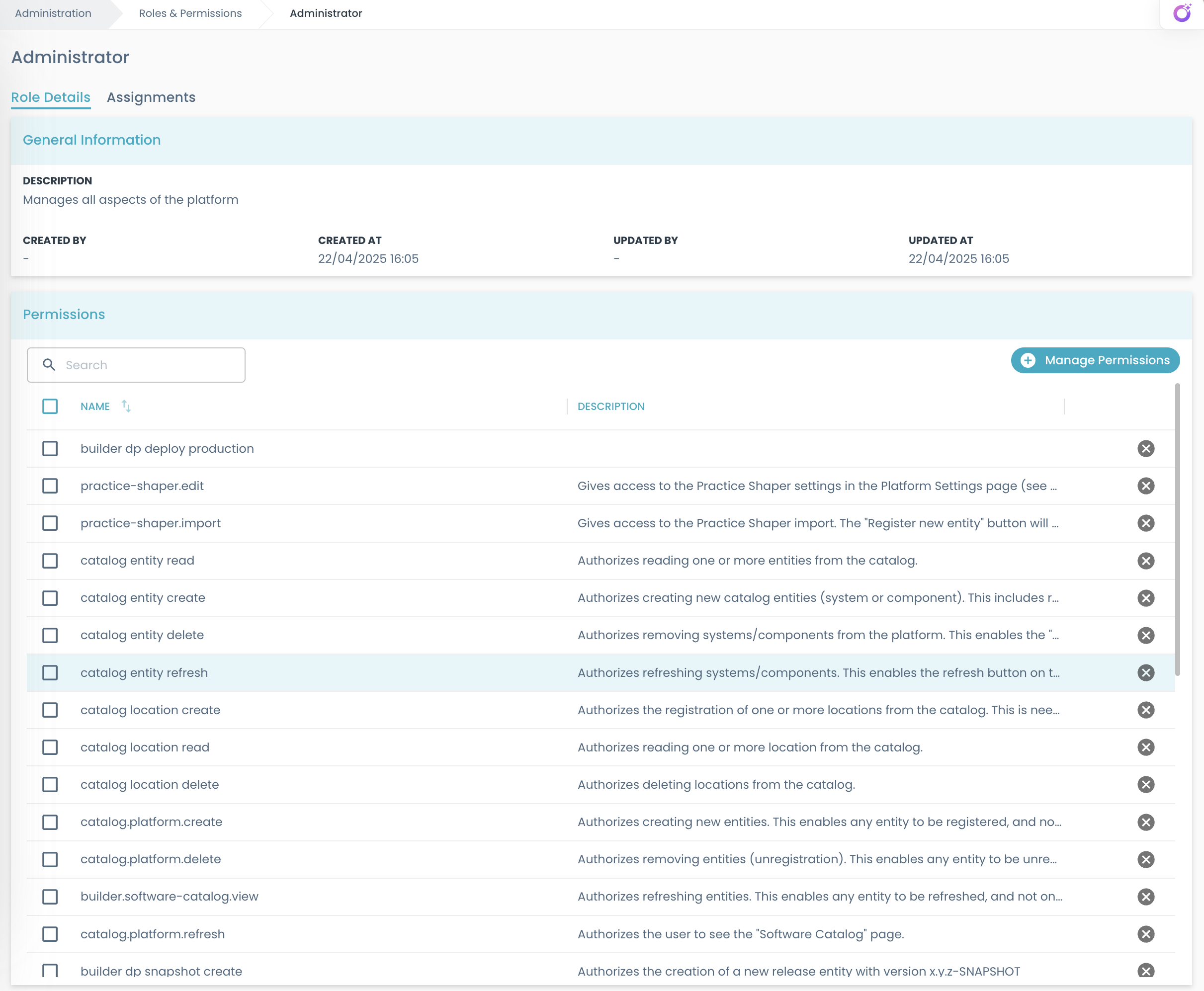
General Information
Each role includes other information:
- Created By: The user who created the role
- Created At: The date and time when the role was created
- Updated By: The last user who modified the role
- Updated At: The date and time of the last modification
These are visible in the detail page.
Binding permissions to a role
To make a role useful, it needs to have some permissions associated to it.
In the Permissions table on the role detail page, all permissions associated with the current role are listed.
If the user has the rbac.role.edit permission, they can add or remove permissions.
To manage permissions for a specific role:
- Navigate to the role’s detail page
- Click the "Manage Permissions" button
- Select or deselect permissions as needed, then apply changes
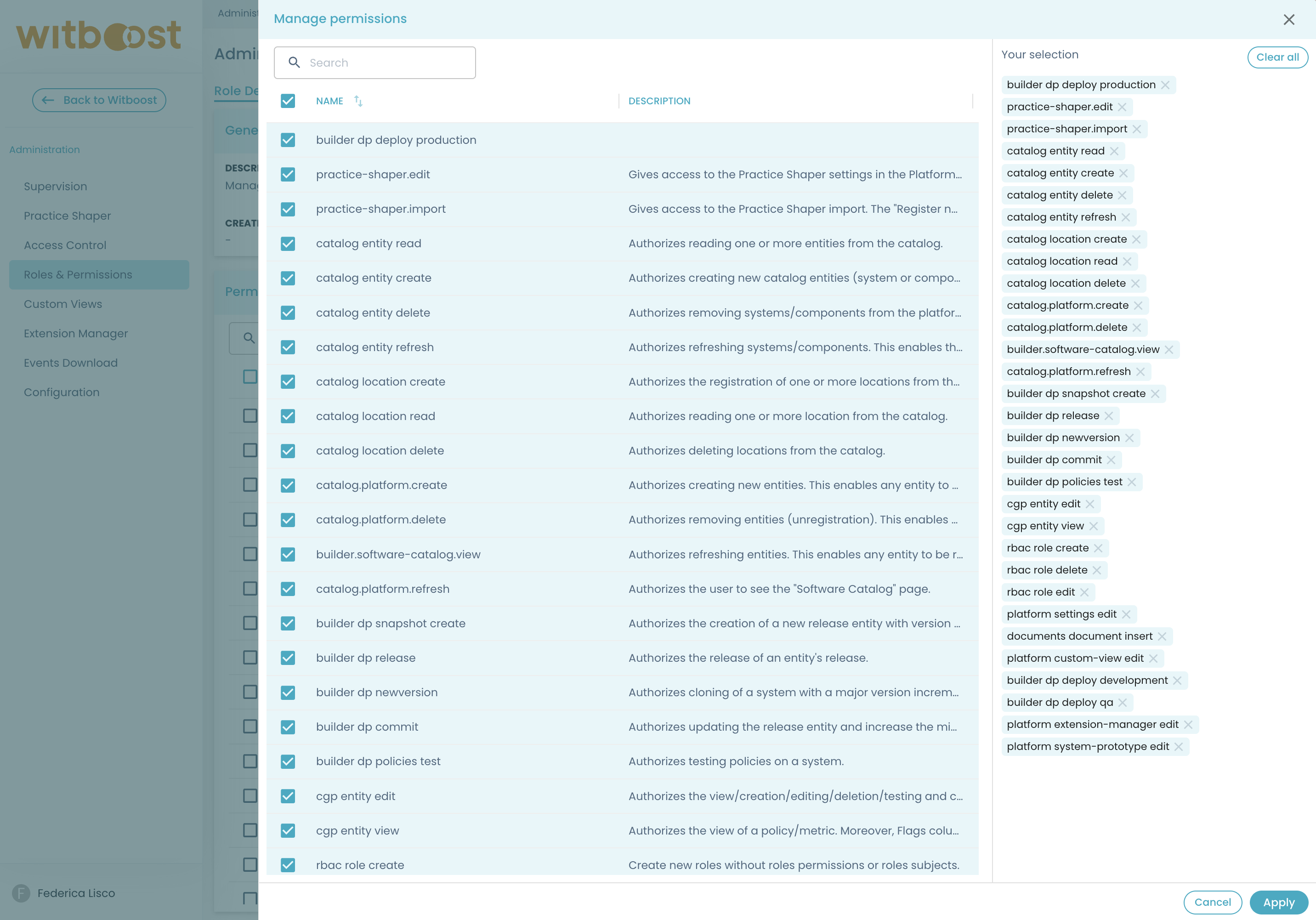
The interface displays your current selection on the right-hand side, making it easy to track which permissions are being added or removed
Granting permissions to a subject
Finally, after creating roles and associating some permissions to them, you can associate subjects to roles, i.e. you grant them some permissions.
A grant is an equivalent word for a role-subject or subject-to-role association expression.
Subjects in Witboost can be users or groups.
Use the Assignments tab to associate users or groups to the selected role and to define the assignment scope. Currently, scopes can be either systems, domains or system types.
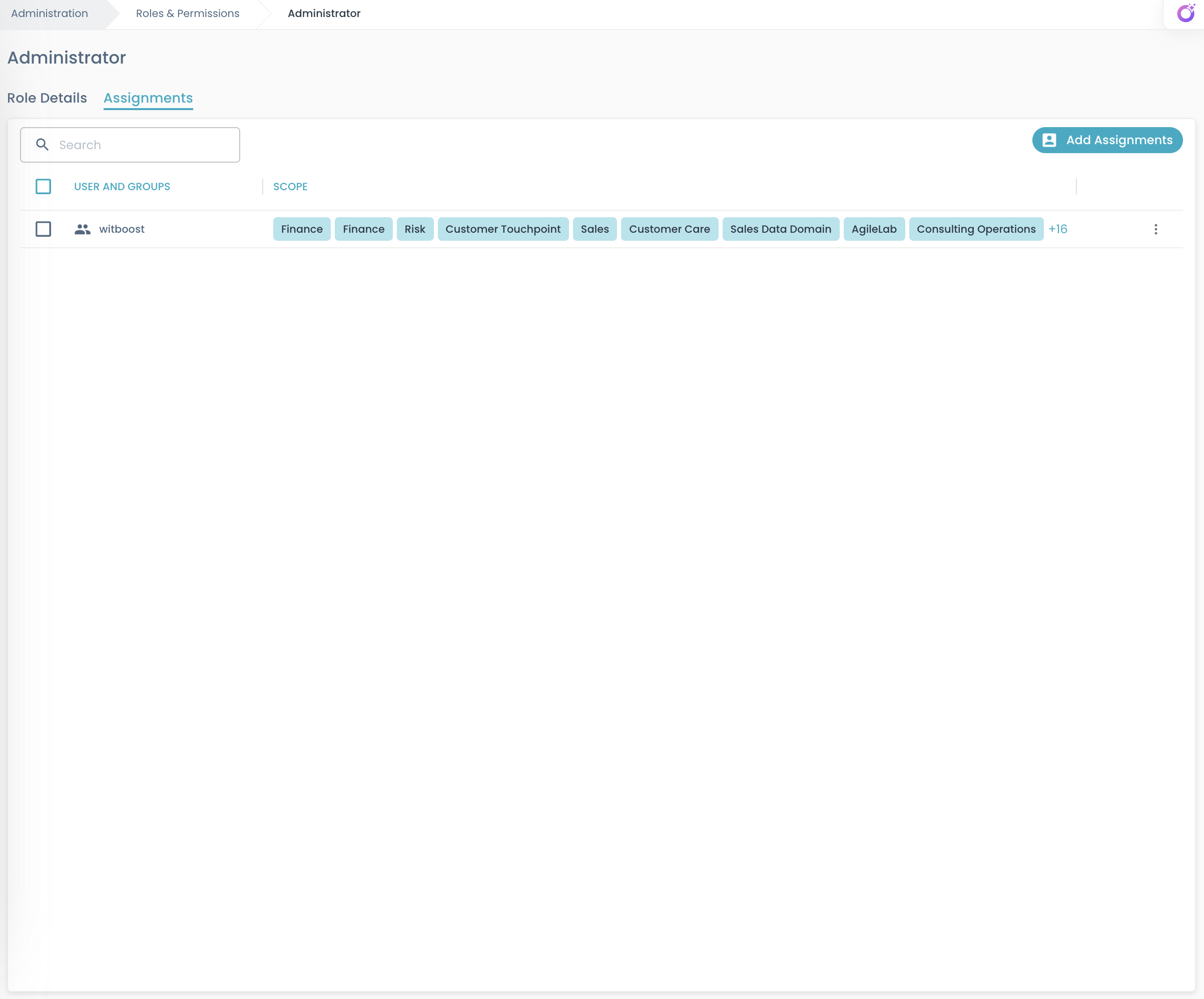
To assign a role to users or groups:
- Click the "Add Assignments" button
- Select users and groups from the dropdown list
- Configure the appropriate scope (by default,
*is applied) - Confirm and apply the changes
Scopes
As of now, scopes become relevant only if your Witboost license includes the Control Plane, since the Control Plane enables resource-level authorization (domains, system types, individual systems).
If your license does not include the Control Plane:
- You don't need to configure scopes at all
- All role assignments automatically apply at global (
*) scope - RBAC still works, but only at a platform-wide level (not domain/system-level granularity)
This behavior may change in the future as additional modules start introducing scope-aware permissions.
The scope of a permission refers to the specific resources or functions to which the permission applies. In other words, it defines the specific areas of Witboost where the permission can be exercised (e.g. User can read only systems within the Finance domain).
Permissions could require a scope, and the set of permissions assigned to a defined role will be usually a mix of permissions that require a scope and others that don't require any scope.
To change the scope of an assignment, use the context menu option "Edit Scope" or select "Enable/Disable Scopes".
This will open a drawer containing toggle buttons for each available scope.
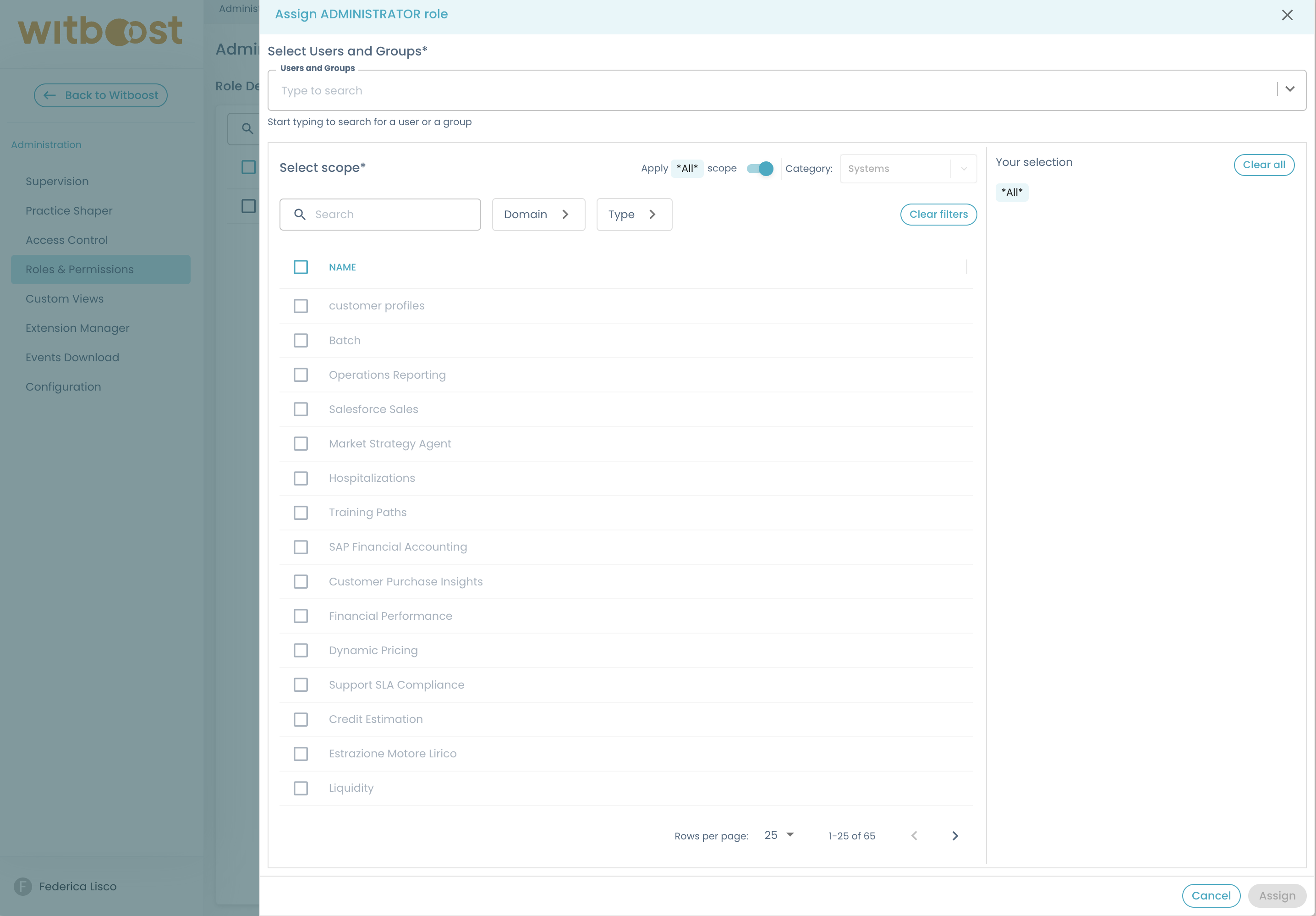
In Witboost, you can assign one of the following types of scopes to a role-subject definition:
- Global scope: (default) Setting to the asterisk wildcard
*will grant the permission on the whole set of witboost entities - Domain scope: representation of a domain entity
- System scope: representation of a system (like a data product) entity
- SystemType scope: representation of a system type
Scopes with a hierarchical relationship behave like an OR rule (a broader scope automatically includes its sub-scopes), whereas scopes with an orthogonal relationship behave like an AND rule (all conditions must be met together):
System and Domain scopes have a hierarchical relationship. For example, if a user is assigned a role with the Finance scope, that role applies across the entire Finance domain as well as all the systems and components within it.
The same hierarchical rule applies between System and System Type.
Domain and System Type instead have an orthogonal relationship: they are independent and do not contain each other. For example, if a user is assigned a role with the Data Product (System Type) scope and the Finance (Domain) scope, they can exercise that role only within the Finance domain, and only on data products.
This diagram illustrates how different scope types can be combined orthogonally:
Examples of Scope Combinations
Here are some practical examples of how different scope combinations work:
Example 1: Domain-Only Scope
- Domain Scope:
Finance - System Type Scope: N/A
- Access: Can access all systems (Data Product, AI Project, etc.) within the Finance domain only
- Cannot Access: Any systems outside the Finance domain
Example 2: System Type-Only Scope
- Domain Scope: N/A
- System Type Scope:
AI Project - Access: Can access AI Project systems across all domains (Finance, Sales, etc.)
- Cannot Access: Systems of other types (Data Product, etc.) even within the same domains
Example 3: Combined Domain + System Type Scope
- Domain Scope:
Finance - System Type Scope:
Data Product - Access: Can only access Data Product systems within the Finance domain
- Cannot Access:
- Data Product systems in other domains (Sales, etc.)
- AI Project systems in Finance domain
- Any systems outside Finance domain
Example 4: System-Specific Scope
- Domain Scope: N/A
- System Type Scope: N/A
- System Scope:
System A - Access: Can access only the specific system "System A" regardless of its domain or type
- Cannot Access: Any other systems, even if they're in the same domain or of the same type
Example 5: System + System Type Scope
- Domain Scope: N/A
- System Type Scope:
Data Product - System Scope:
System A - Access: Can access all Data Product systems (including "System A" and any other Data Product systems)
- Cannot Access:
- Systems of other types (AI Project, etc.)
- Any other systems outside the specified scope
Example 6: Multiple Domains + Multiple System Types Scope
- Domain Scope:
Finance,Sales - System Type Scope:
Data Product,AI Project - Access: Can access Data Product and AI Project systems within both Finance and Sales domains
- Cannot Access:
- Systems in other domains (Marketing)
- Any systems outside the specified domain and system type combinations
Example 7: Global Scope
- Domain Scope: N/A
- System Type Scope: N/A
- System Scope: N/A
- Access: Full access to all resources across the entire platform
Creation Templates and Blueprints
If you want to restrict the visibility of a Creation Template or Blueprint to users with access (through RBAC scopes) to a specific domain, just place a reference to the domain inside spec.domain property.
Take as an example the blueprint's descriptor below:
apiVersion: agilelab.it/v1alpha1
kind: Blueprint
metadata:
name: test-blueprint
title: Test Blueprint
description: Create a Test Blueprint
tags:
- test
spec:
lifecycle: experimental
owner: group:test
domain: domain:finance
# ...other properties...
When instead the RBAC scope includes a system type:
- Users can only access system templates where the
spec.generatesproperty either matches the system type or is not defined. - Users can only access component templates where the
spec.generatesproperty either matches a component type child of the system type (see Practice Shaper) or is not defined. - Users can only access blueprints whose main system template has a
spec.generatesproperty that matches the system type or is not defined.
Example 1: System Template
- Template Type: System
- spec.domain:
domain:finance - spec.generates:
systemtype:dataproduct
| Scope | Access Result |
|---|---|
[domain:finance] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:finance, systemtype:aiproject] | ❌ Not Allowed |
[systemtype:dataproduct] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:finance, systemtype:dataproduct] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:marketing, systemtype:dataproduct] | ❌ Not Allowed |
Example 2: Component Template
- Template Type: Component
- spec.domain:
domain:finance - spec.generates:
componenttype:storage(part ofsystemtype:dataproduct)
| Scope | Access Result |
|---|---|
[domain:finance] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:finance, systemtype:package] | ❌ Not Allowed |
[systemtype:dataproduct] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:finance, systemtype:dataproduct] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:marketing, systemtype:dataproduct] | ❌ Not Allowed |
Example 3: Blueprint
- spec.domain:
domain:marketing - Main Template spec.generates:
systemtype:dataproduct
| Scope | Access Result |
|---|---|
[domain:marketing] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:marketing, systemtype:package] | ❌ Not Allowed |
[systemtype:dataproduct] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:marketing, systemtype:dataproduct] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:finance, systemtype:dataproduct] | ❌ Not Allowed |
Example 4: System Template with Only spec.generates
- spec.domain: N/A
- spec.generates:
systemtype:dataproduct
| Scope | Access Result |
|---|---|
[domain:finance] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:finance, systemtype:package] | ❌ Not Allowed |
[systemtype:dataproduct] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:finance, systemtype:dataproduct] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:marketing, systemtype:dataproduct] | ✅ Allowed |
Example 5: System Template with Only spec.domain
- spec.domain:
domain:finance - spec.generates: N/A
| Scope | Access Result |
|---|---|
[domain:finance] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:finance, systemtype:package] | ✅ Allowed |
[systemtype:dataproduct] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:finance, systemtype:dataproduct] | ✅ Allowed |
[domain:marketing, systemtype:dataproduct] | ❌ Not Allowed |
Witboost Permissions
Below we dive into each Witboost module and understand which are all the available permissions. You will also find some cookbooks that facilitate the definition of permissions based on use cases.
Practice Shaper
Learn about the Practice Shaper in the dedicated section of the documentation.
| Permission | Description | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| practice-shaper.edit | Gives access to the Practice Shaper settings in the Platform Settings page (see platform.settings.edit permissions below) | none |
| practice-shaper.import | Gives access to the Practice Shaper import. The "Register new entity" button will show. | none |
Entities Registry
Most of the operations done by Witboost under the hood leverages the Witboost Entities registry (e.g. operations on systems, components, resources, users, groups, domains and templates). Hence, most actions done by end users will require them to have permissions to interact with the Witboost Entities registry.
The entities registry works with two objects:
- Entities: these are systems, components, resources, users, groups, domains and templates. But not Governance policies or Marketplace items
- Locations: there are the URLs or paths to the
catalog-info.yamlthat generate the corresponding entity. e.g. for a data product, the location corresponds to the URL that points to thecatalog-info.yamlin the data product's repository. The catalog will periodically process each location and regenerate all entities so that they stay up-to-date with what is found from the origin location.
The actions that a user can take on the entities registry are:
- Read/Add/Delete/Refresh entities in the registry
- Read/Add/Delete locations in the registry
Adding locations and adding entities might be misleading or confuse the user. When you create a system or an output port from a template, you are creating a repository and then adding the location of that repository in the entities registry. Then, the entities registry will process the new location and will generate the corresponding entity from the catalog-info.yaml.
What you see in the entities page is the list of entities that have been already processed. This is why sometimes the entity that you just created is not yet visible in the entities registry because its location has not been already processed.
Entities Registry Permissions
In this section, we will describe what permissions are present in the Entities Registry. These permissions can be assigned to roles defined by the platform team.
| Permission | Description | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| catalog.entity.read | Authorizes reading one or more entities from the catalog. | Catalog Entity URN |
| catalog.entity.create | Authorizes creating new catalog entities (system or component). This includes registering existing systems/components from the related button. | none |
| catalog.entity.delete | Authorizes removing systems/components from the platform. This enables the "Unregister Entity" button. | Catalog Entity URN |
| catalog.entity.refresh | Authorizes refreshing systems/components. This enables the refresh button on the detail pages. | Catalog Entity URN |
| catalog.location.create | Authorizes the registration of one or more locations from the catalog. This is needed when registering an existing component into the catalog or scaffolding a new one. | none |
| catalog.location.read | Authorizes reading one or more location from the catalog. | none |
| catalog.location.delete | Authorizes deleting locations from the catalog. | none |
| catalog.platform.create | Authorizes creating new entities. This enables any entity to be registered, and not only project ones. This permission also requires the catalog.entity.create permission to be enabled. Moreover, this permission enables the Template Editor link. | none |
| catalog.platform.delete | Authorizes removing entities (unregistration). This enables any entity to be unregistered, and not only project ones. This permission also requires the catalog.entity.delete permission to be enabled. | none |
| catalog.platform.refresh | Authorizes refreshing entities. This enables any entity to be refreshed, and not only project ones. This permission also requires the catalog.entity.refresh permission to be enabled. | none |
| platform.settings.edit | Authorizes the view/use of the platform settings page. Who can view the settings page can also edit them, there is no distinction yet. Additionally, it grants the ability to view the "Entities" section. | none |
| builder.software-catalog.view | Authorizes the user to see the "Entities", "Templates" and "User and Groups" pages. | none |
You will likely have roles that will mix entities registry permissions with builder permissions, thus refer to the Builder Module section below to clarify which permissions are needed in the day-to-day workflows in Witboost.
Builder Module�
The main operations that a user can perform on the Builder module are:
- Create a system/component using a template, e.g. a data product
- Create a new system version
- Register an existing system/component
- View the entities/project tab and their details
- Build and deploy: test policies, create a draft release, update/promote the release, deploy/undeploy a release
- Create a new system prototype
Builder Permissions
In this section, we will describe what permissions are present in the Builder module. These permissions can be assigned to roles defined by the platform team.
| Permission | Description | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| builder.dp.snapshot.create | Authorizes the creation of a new release entity with version x.y.z-SNAPSHOT | Catalog Entity URN |
| builder.dp.release | Authorizes the release of an entity's release. | Catalog Entity URN |
| builder.dp.deploy.{env} | Authorizes deploy action on a system. You can specify a permission for each environment. | Catalog Entity URN |
| builder.dp.newversion | Authorizes cloning of a system with a major version increment | Catalog Entity URN |
| builder.dp.commit | Authorizes updating the release entity and increase the minor version. | Catalog Entity URN |
| builder.dp.policies.test | Authorizes testing policies on a system | Catalog Entity URN |
| builder.system-prototype.edit | Authorizes testing policies on a system | Catalog Entity URN |
As you can notice, there is no 1 to 1 mapping between the main operations described and the permissions available in this table. This is because each operation most of the time involves more than one permission to be authorized.
Builder Permissions Cookbook - General
This cookbook can be used by the Platform team as a reference when configuring RBAC. For each action listed in the table, there will be a list of permissions needed. This table will indicate if the action also requires a scope. If you are in doubt about which scope to set, read the Scopes section above.
| Action | Description | Permissions Needed | Requires Scope? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Use a template (e.g. Create a project/component) | Create a project/component by using a template | catalog.entity.read, catalog.location.create, catalog.entity.refresh | Yes |
| Register an existing project/Component/Template | Register an existing project/Component/Template by using the Builder > Register Existing Component feature | catalog.entity.create, catalog.location.create | No |
| View systems/components and their details | See a list of available entities in Witboost (e.g. a data product) and access their details | catalog.entity.read, catalog.location.read | Yes |
| View templates list | View the list of registered templates in Witboost | catalog.entity.create | No |
| Triggering an entity refresh | Refresh an entity by clicking on the refresh button in the About card of any project or component | catalog.entity.refresh | Yes |
| View the entities list in administration page | View the entities list in administration page | builder.software-catalog.view, platform.settings.edit | No |
Builder Permissions Cookbook - Release Management
User must be already authorized to view the project and hence, the Edit and Test and Deployment tabs. The required permissions described below will still list permissions needed as if the user is not already authorized to view the project.
| Action | Description | Permissions Needed | Requires Scope? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create New Draft Release | Create a new draft release for a project | catalog.entity.read, catalog.entity.refresh, catalog.location.create, builder.dp.snapshot.create | Yes |
| Promote a Draft Release | Promotes a draft release into a release | catalog.entity.read, catalog.entity.refresh, builder.dp.release | Yes |
| View all project's releases | View the list of releases for a project | It is implicitly granted when a user can view a project | N/A |
| Create a new project version | Create a new project version that is a clone of the existing one | catalog.entity.read, catalog.location.create, builder.dp.newversion | Yes |
| Update a Draft Release | Commits latest changes by updating the draft release | catalog.entity.read, catalog.entity.refresh, builder.dp.commit | Yes |
| Get a preview descriptor | Get preview descriptor of a project | catalog.entity.read, catalog.entity.refresh | Yes |
| Test policies compliance | Test if a project is compliant with governance policies | catalog.entity.read, catalog.entity.refresh, builder.dp.policies.test | Yes |
| Deploy/Undeploy a project | Deploy/Undeploy a project's release to a specific environment | catalog.entity.read, catalog.entity.refresh,builder.dp.deploy.{env} | Yes |
Witboost Computational Governance Module
The main operations that a user can perform on the WCG (Witboost Computational Governance) module are:
- View governance policies/metrics
- Create governance policies/metrics
- Delete governance policies/metrics
- Edit governance policies/metrics
Witboost Computational Governance permissions
In this section, we will describe what permissions are present in the WCG module. These permissions can be assigned to roles defined by the platform team.
| Permission | Description | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| cgp.entity.edit | Authorizes the view/creation/editing/deletion/testing and change status of a policy/metric. Moreover, Flags column in marketplace is visible and Flag and Score dialog is accessible. | none |
| cgp.entity.view | Authorizes the view of a policy/metric. Moreover, Flags column in marketplace is visible and Flag and Score dialog is accessible. | none |
Marketplace Module
The main operations that a user can perform on the Marketplace module are:
- View the Marketplace Search page with all systems/output ports and their details
- View the Marketplace Visual Discovery
- Access Mesh Supervision
- Send an access request to a project's output port
- Give access to a project's output port
- Write a review on a project
- Ask questions on a project
- Answer questions on a project
At the moment all operations described above are, by default, granted to any user of Witboost. The only exception is made by those who can give access to a project's output port or who can answer a question, that is safe by design since only the project owner will receive the request, and hence is the only one that can answer to that.
RBAC Module
In this section we will describe what permissions are present in the RBAC plugin of the platform. These permissions can be assigned to roles defined by the platform.
These permission relate to the authorization system of Witboost, enabling adding or removing roles assignments as well as roles permissions. Assign these permissions only to highly-privileged roles like Administrator.
| Permission | Description | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| rbac.role.create | Create new roles without roles permissions or roles subjects. | none |
| rbac.role.delete | Delete user roles. | none |
| rbac.role.edit | Update existing roles and assigning roles permissions or roles subjects. Disabling of Authenticated Guest Users. | none |
Other Platform permissions
All other useful platform permissions can be found in this section. These permissions can be assigned to roles defined by the platform team.
| Permission | Description | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| platform.settings.edit | Authorizes the view/use of the platform settings page. Who can view the settings page can also edit them, there is no distinction yet. | none |
| documents.document.insert | Authorizes the insertion of a document into the database through its respective route. Refer to the documents documentation page for more information. | none |
| platform.custom-view.edit | Can see and use the download button for Custom Views, and use the REST API to add a new custom view. | none |
| platform.extension-manager.edit | Can use the extension manager REST API to perform edit operations. Can access the extension manager admin section. | none |
| platform.users.auth.invalidate-tokens | Can invalidate the access tokens issued for a specific user. | none |
| platform.users.service-accounts.edit | Can create, edit and delete service accounts in the administration panel. | none |
| platform.users.service-accounts.access-tokens.edit | Can manage access tokens for service accounts in the administration panel. | none |